Basic Spelling and Phonics Edition

The “Sawaru Glyph Phonics Edition” is the foundational material used at the beginning of the Sawaru Glyph program. It incorporates tactile reading practice using video and audio resources aligned with phonics and syllables. Starting with single letters of the alphabet, progressing to simple sound spellings, and then to more complex sound spellings, this approach builds memory for letter forms and spellings step by step.
The process not only strengthens letter form memory but also facilitates the formation of word-form memory from spellings, promoting fluent reading. Additionally, it supports the formation of associative memory between spellings and sounds.
Product
Product Contents:
・Alphabet 26 letters (1 sheet)
・One Letter One Sound group (5 sheets)
・Vowel Digraphs group (3 sheets)
・Consonant Digraphs group (3 sheets)
・Blending Sounds group (7 sheets)
・Sight Words (3 sheets)
・Video and audio specialized for tactile reading
・Instruction manual for using Sawaru Glyph
・Test paper for measuring learning outcomes
Audio-Visual Materials for Tactile reading Learning
These are dedicated audio-visual materials designed for tactile reading learning. English words are first marked up and then read aloud. Learners retain phonological information in their working memory while engaging in tactile reading of the three-dimensionalized words. This learning method strengthens the connection between spelling and sound, enhancing decoding skills.
User Manual and Evaluation Sheets:
Sawaru Glyph has been developed to enable functional training for dyslexia at home. The included instruction manual provides detailed guidance on how to use the materials. Additionally, evaluation sheets are provided to measure changes in reading skills and RAN functionality resulting from Sawaru Glyph. This allows families to conduct scientifically-based training at home.
Product features of the Phonics Edition
Basic Spelling and Phonics Edition is the foundational material that Sawaru Glyph users should start with. In this program, users study three-dimensional words while watching and listening to dedicated audiovisual content, combining touch and oral reading.
This material provides step-by-step tactile reading practice, following phonics rules. It begins with simple sound spellings, progresses to more complex sound spellings, and eventually covers sight words. By leveraging haptic effects, it strengthens the integration of spelling and sound memory. Additionally, chunking spellings helps form word-shape memory.
Stages and Levels of the Material
.png)
Before using the Highly Imaginable Words and Short Sentences Edition, the phonics edition is used to build basic spelling and sound memory. Through this process, users acquire spelling and sound rules and establish the foundation for word-shape memory.
In the Highly Imaginable Words and Short Sentences Edition, the goal is to further strengthen word-shape memory and promote RAN (Rapid Automatized Naming).
Target Learners
.png)
- Children and adults with dyslexia
This material is designed for individuals who struggle to read fluently, feel fatigued when reading, or have difficulty accurately remembering spellings. It is suitable for a wide range of users, from children to adults. - Typically developing children, non-native English-speaking children, and adults
This material (Phonics Edition) is not only for individuals with dyslexia who experience reading difficulties but is also suitable for anyone who wants to efficiently learn the rules of spelling and sound.
How to Use
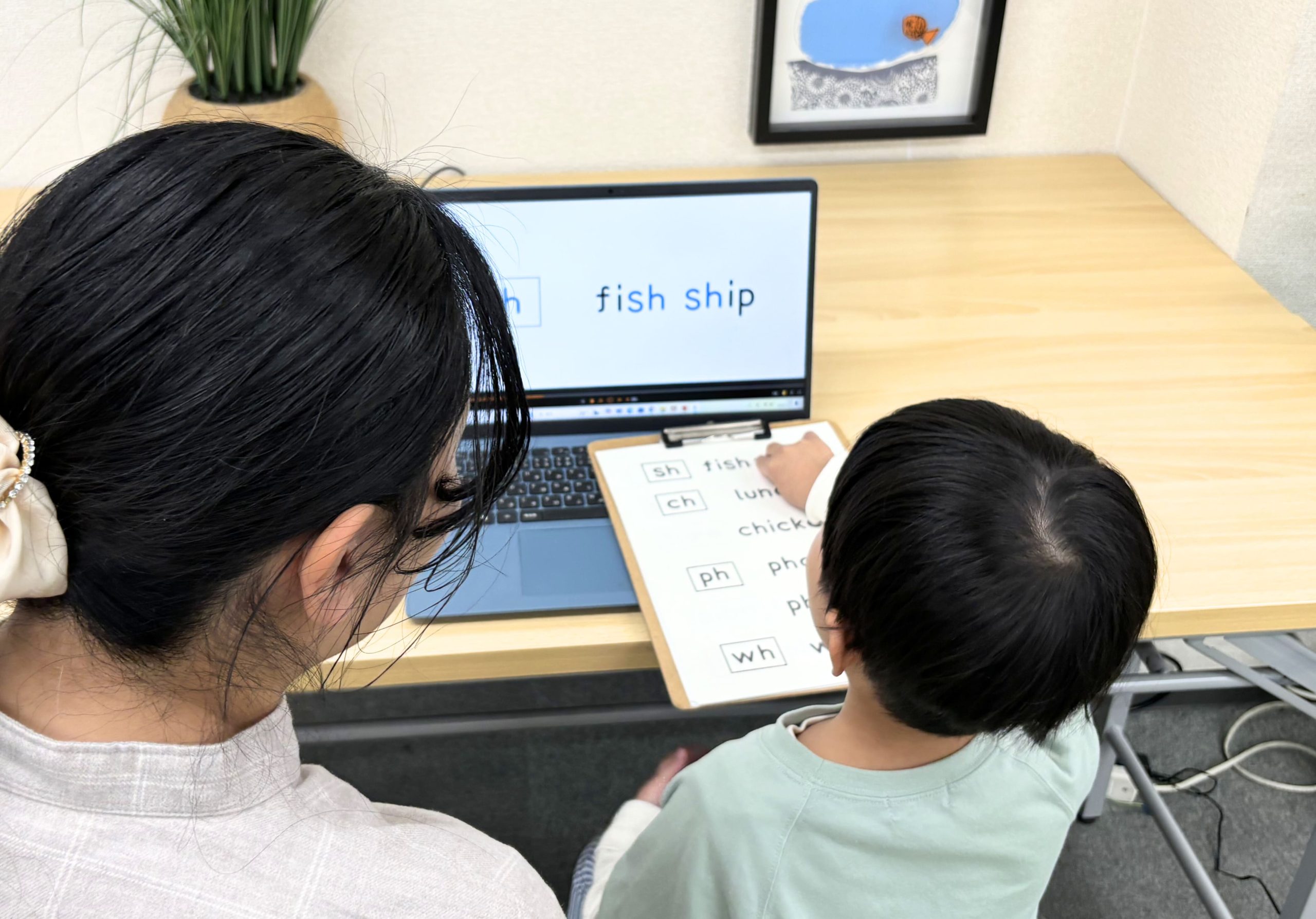

- Immediately after watching the visual-audio presentation of a word, touch and read aloud the three-dimensional English word while looking at it.
- Begin tactile reading learning with simple spellings and gradually progress to complex spellings and sight words, following phonics rules based on the forms of alphabetic letters.
- A daily learning session consists of 5 to 6 sheets, taking about 15 minutes. You can study a little every day.

You are welcome to contact us for a free consultation about how to use the product or whether it is suitable for your needs—even before making a purchase. Keisuke Miyazaki, a licensed speech-language therapist, will respond to your inquiry by email.
Please include the following information in your message:
-
Age of the person who will use the product
-
Current status of reading and spelling skills
-
Difficulties currently being faced (e.g., in school, at work, or other areas)
-
Whether the person has any developmental disorders, including learning disabilities
Principles and Effects
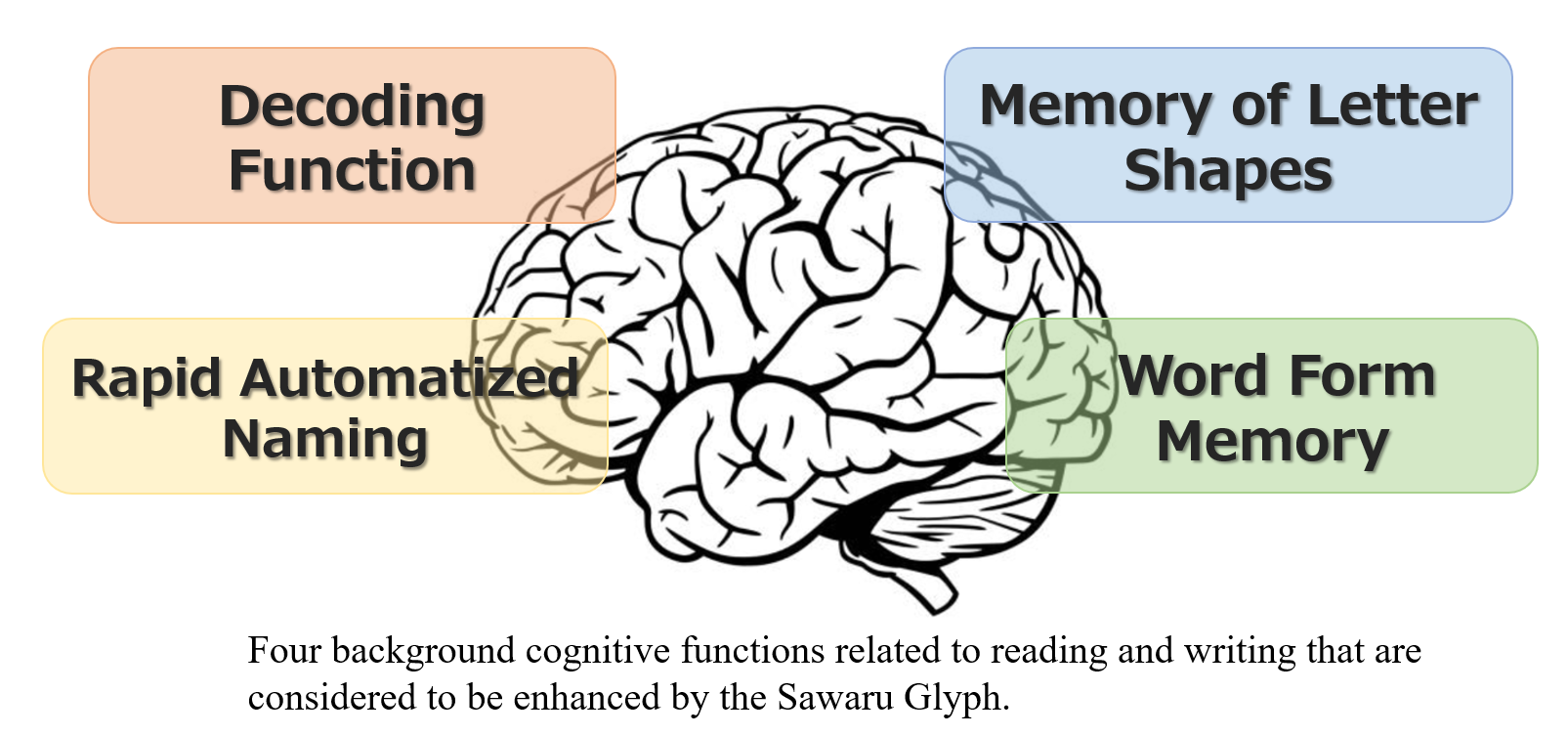
By utilizing the effects of haptics, Sawaru Glyph promotes fluent reading and enhances four cognitive functions related to letter recall. It helps improve the cognitive vulnerabilities of dyslexia.
Haptics has the following three functions:
- Haptic feedback enhances attention to the target and strengthens memory traces.
- Haptics integrates with visual information in the brain to form concrete, multimodal images.
- Haptics possesses characteristics of both visual representation (parallel) and phonological representation (sequential), serving to connect the two.
By utilizing these functions of haptics, the neural networks involved in reading and writing abilities in the brain are strengthened.
1. Formation of a precise and robust mental image of letter shapes
It has been found that not only seeing letters and symbols, but also engaging with them through haptics while seeing promotes awareness of their shapes, enhancing memory images. By utilizing haptics to interact with the letters, attention is more strongly focused on their shapes, making it easier to leave memory traces. Furthermore, research shows that haptics and vision share a common neural basis in the brain and are cognitively integrated. Incorporating haptics allows for multi-sensory memory encoding.
2. Formation of word form memory (chunking)
By receiving haptic feedback on the spelling (sequence of letters) while reading, chunking of letter sequences in memory is promoted. This enables efficient formation of word form memory. Once the word form memory is established in the mind, it becomes easier to read texts.
3. Formation of associative memory between letters and sounds
Dyslexia often involves difficulty in associating letters with sounds. While memory formation between letters and sounds is promoted by reading aloud alone, the process is further enhanced by combining it with the video and audio resources used in the tactile reading program. By providing simultaneous haptic (touch-based) interaction with letters and auditory information, more effective formation of associative memory between letters and sounds is achieved.
4. The Effect of RAN (Rapid Automatized Naming) Enhancement
RAN(Rapid Automatized Naming) refers to the ability to efficiently retrieve and name visual information, such as pictures or numbers. It is known that children with dyslexia tend to have lower naming speed. Sawaru Glyph is the first program in the world to confirm the improvement of RAN through tactile reading practice. A hypothesis suggests that reading meaningful words while engaging in tactile interaction enables the creation of a bypass within the semantic network, linking the visual lexicon associated with letter and word forms and the phonological lexicon tied to spoken words. This bypass improves the recall of letter forms, which serves as a cognitive cue to facilitate the recall of words (phonological information).
Technology and Copyrights
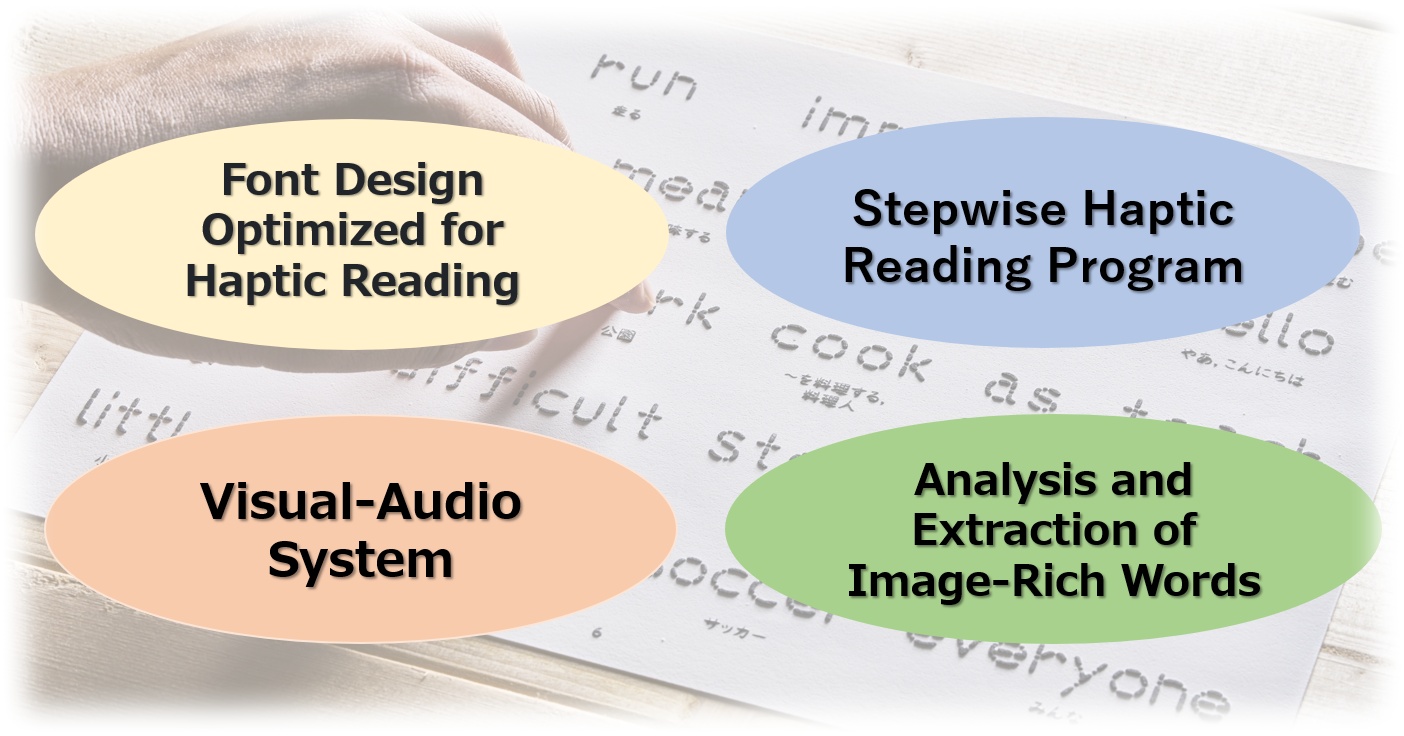
Sawaru Glyph is not merely a teaching material for tactile reading of embossed letters.
This tool integrates the following four original technologies to enable effective multisensory learning through the use of haptics:
- Font Design Optimized for tactile reading
- Audio-Visual Features for Integrating Spelling and Sound
- Stepwise tactile reading Program
- Analysis and Selection of Image-Rich Words
These technologies support effective learning by utilizing fonts designed for tactile reading and developing audio-visual systems that enhance the connection between letters and sounds. Additionally, the words used in the materials are carefully selected to prioritize semantic processing and facilitate the formation of reading and writing networks.
These technological innovations are protected by international copyrights.
For more details, please refer to the “Technology and Copyrights” page.

